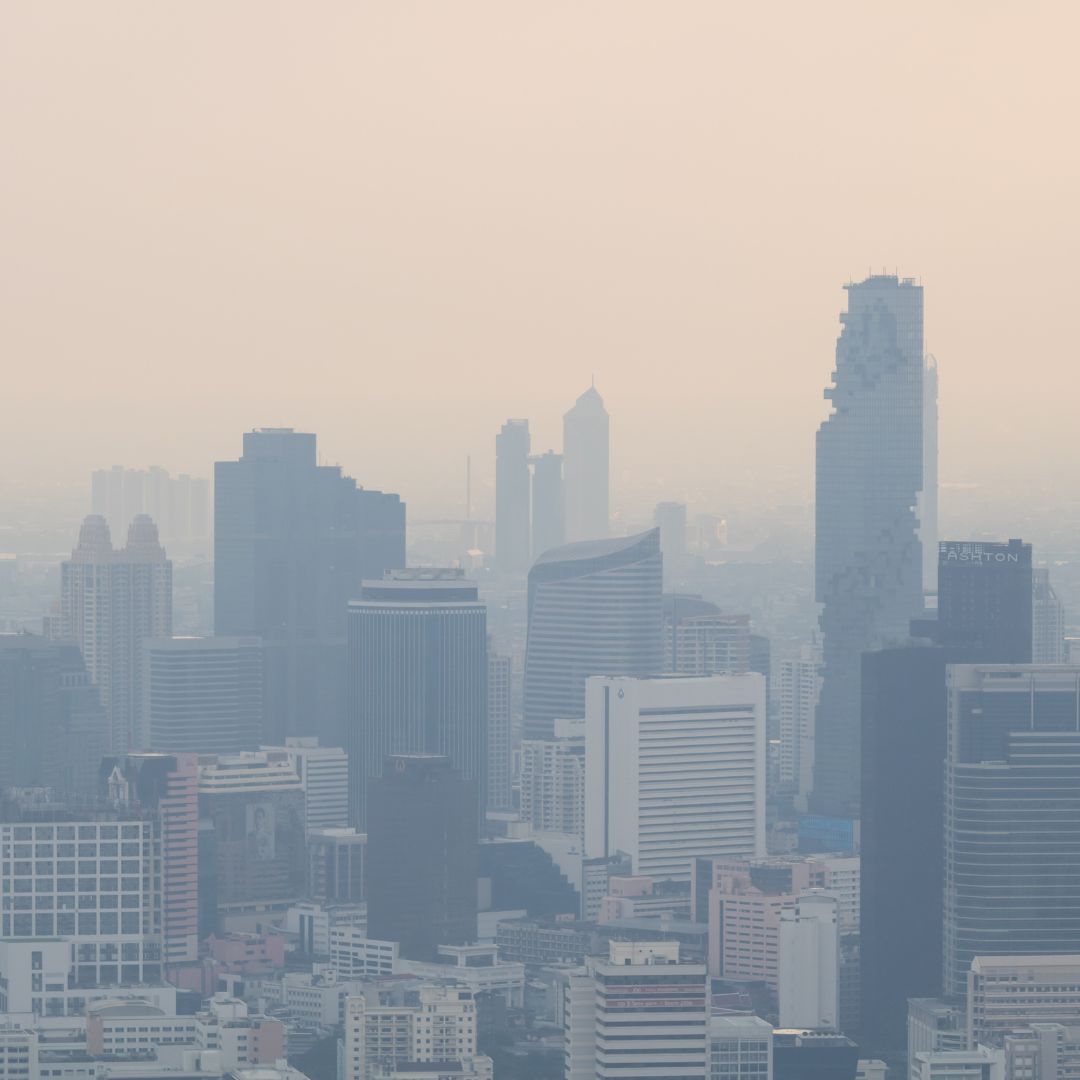
The Costly Cloud: How Air Pollution Impacts the Economy
Air pollution, the silent assailant lurking in our atmosphere, poses a grave threat to both public health and the economy. While the immediate impact on human well-being is evident, the long-term repercussions on economic stability and growth are equally concerning. In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted ways in which air pollution adversely affects the economy, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive action.
Health Costs:
One of the most direct and tangible consequences of air pollution is its detrimental effect on public health. Exposure to harmful pollutants leads to respiratory ailments, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature deaths. As healthcare systems struggle to cope with the increased demand for medical assistance, the accompanying costs skyrocket. These mounting healthcare expenses put a strain on public budgets, leaving less room for investment in vital sectors such as education and infrastructure.
Reduced Labor Productivity:
Unhealthy air quality takes a toll on workforce productivity, thereby hindering economic growth. Employees exposed to high levels of pollutants are more likely to suffer from respiratory problems and allergies, leading to increased absenteeism and decreased productivity. Moreover, studies have shown that air pollution can impair cognitive abilities, diminishing decision-making skills, and overall efficiency. This decline in labor productivity dampens economic output and competitiveness, adversely affecting both businesses and national economies.
Agricultural Productivity:
The impact of air pollution extends far beyond urban centers. Pollutants such as ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter harm crops, forests, and ecosystems. Reduced agricultural productivity not only leads to lower yields and food shortages but also causes price hikes in the market. Farmers bear the brunt of this, facing economic losses while trying to adapt to changing environmental conditions. Furthermore, the ripple effects of diminished agricultural output affect food processing industries, leading to job losses and economic instability in rural areas.
Tourism and Recreation Decline:
Clear skies and fresh air are often key factors that attract tourists to a destination. However, areas plagued by air pollution suffer a decline in tourism and recreational activities. Visitors are discouraged from exploring regions with poor air quality, impacting revenue streams for hotels, restaurants, and local businesses. Moreover, outdoor recreational activities, such as hiking, biking, or enjoying parks, become less appealing, leading to a decline in associated industries. The resulting economic downturn further exacerbates the negative cycle of air pollution’s impact.
Environmental Damage and Cleanup Costs:
Air pollution contributes to environmental degradation, including acid rain, smog, and the deterioration of ecosystems. Cleaning up polluted areas, restoring damaged environments, and implementing effective pollution control measures all incur substantial costs. Governments and communities must allocate resources to combat environmental damage caused by air pollution, diverting funds that could be used for infrastructure development or education initiatives.
Regulation and Compliance Costs:
Governments worldwide impose regulations and standards to curb air pollution, requiring industries to invest in pollution control technologies and adjust their production processes. Compliance with these regulations involves significant costs, including the installation of emission control equipment, continuous monitoring systems, and operational changes. While these measures are essential for public health and environmental preservation, the associated expenses impact business profitability and economic growth.
Reputation and Investment:
Regions marred by high levels of air pollution suffer from a tarnished reputation, deterring potential investors. Businesses may hesitate to establish operations in polluted areas due to concerns over employee health, reduced productivity, and negative public perception. The subsequent decline in investment opportunities limits job creation and economic growth in these regions, perpetuating a vicious cycle of stagnation.
Tackling Air Pollution for Sustainable Prosperity:
Air pollution, often underestimated as a mere environmental issue, poses significant threats to the economy. The detrimental effects on public health, labor productivity, agricultural output, tourism, energy consumption, environmental integrity, and investment opportunities underscore the urgency of combatting this invisible menace. Policymakers, businesses, and individuals must prioritize sustainable practices, embrace cleaner technologies, and implement stringent pollution control measures to safeguard public health, enhance productivity, and foster long-term economic prosperity. Only by addressing air pollution comprehensively can we create a healthier, more sustainable future for generations to come.