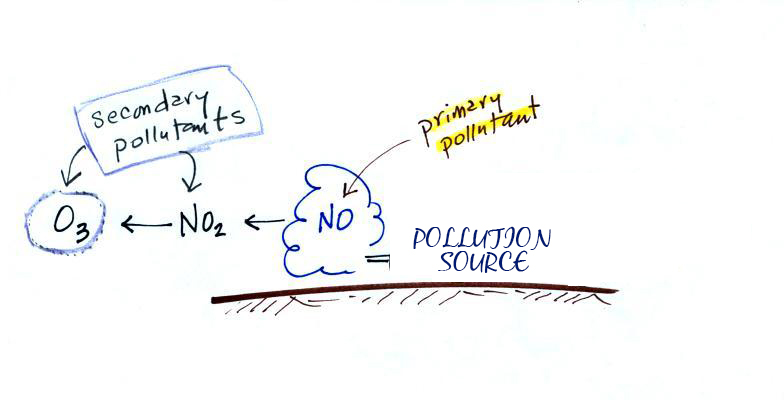
Secondary Pollutants
All the gaseous pollutants are primary pollutants. These pollutants are emitted directly and such are not found in the atmosphere. Instead, they form as a result of the pollutants emitted from these sources reacting with molecules in the atmosphere. Pollutants that are emitted into the environment from a source called Primary pollutants. There are also secondary pollutants which are formed in the atmosphere.
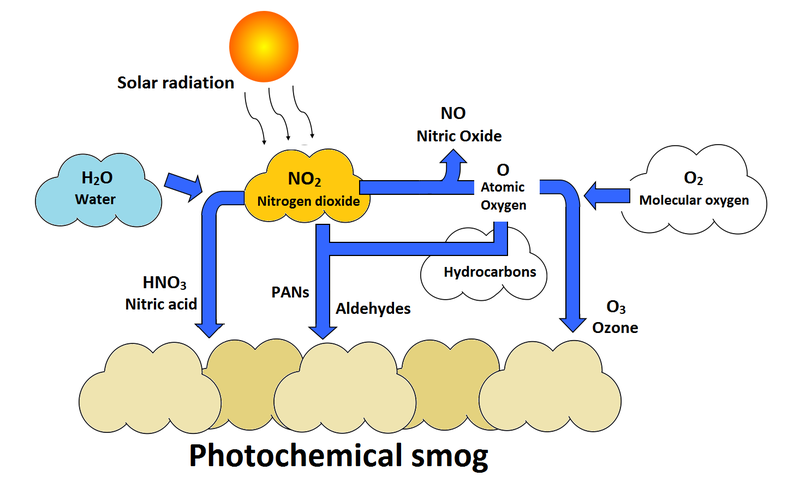
Secondary pollutants are those which are formed in the air due to interaction of primary air pollutants among themselves or by reaction with normal atmospheric constituents like sunlight, water vapor etc. With or without photo activation. For example ozone, formaldehyde, peroxy – acetyl nitrate and acidic mist like H2SO4 (SO2 + moisture), smog, photochemical smog.
Evidences and experiments indicate that exhaust gases of automobiles have particular importance in the formation of secondary pollutants For example
Nitrogen oxide produced in the combustion of petroleum and other fuels emitted to the atmosphere, yield ozone in the presence of sunlight. It is to be noted that ozone is not emitted as such to the atmosphere but formed only from primary pollutants by the interaction in the atmosphere and thus constitute of secondary pollutants. The ozone produced reacts with hydrocarbons to form a series of compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, organic acids, acyl nitrates and epoxy compounds. This types of photochemical reactions usually occur in smog. The term ‘ smog’ denotes a mixture of smoke and fog .it is reported that during a smog , the concentration of ozone and oxidant material are found to be high . According to the Haagen – smit theory , ultraviolent rays in the sunlight break the nitrogen dioxide molecule to form nitric oxide and atomic oxygen . These products react with molecular oxygen to form ozone. The reaction may be represented as follows
- NO2 – NO + O
- O2 + O – O3
- NO + O2 – NO3
- NO3 + O2 – NO2 + O3
- 2NO2 + O3 – N2O5 + O2
- NO + O3 – NO2 + O2
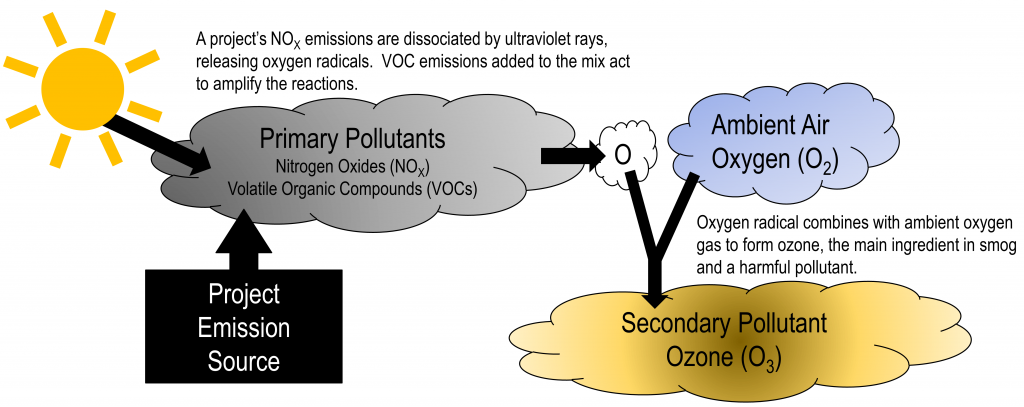
The liberated molecular oxygen reacts with molecules, of aldehydes and Oxy- genated organic compounds. which are activated by the absorption of light .
RCOOOH+O2 – RCOOH + O2
Thus once again ozone is liberated as a by product. On absorption of light energy, some of the aldehydes and ketones become free radicals. They react with molecular oxygen as follows
HCO + O2 – HCO3
The free radical HCO3, reacts further with molecular oxygen, nitric oxide and hydrocarbons as Follows
HCO3 + O2 – HCO2 + O3
HCO3 + NO – HCO2 + NO2
The cycle reaction is set in motion and numerous products are formed. It is to be noted that ozone and nitrogen dioxide are evolved continuously throughout the cycle of reaction. Free radicals lead to several other types of free radicals reaction and polymerization and oxidation chain reaction.
Though these reaction are studied well, the chemistry of photochemical smog is still not clearly understood. Many attempts have been made to reduce the level of ozone in the atmosphere. Actually, if the amount of hydrocarbons released in the atmosphere is reduced, then the ozone formed will be utilized in the oxidation of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide. But unfortunately the level of ozone have never decreased and the puzzle has not yet been solved .