Particulate Pollutants
Pollutant is a substance present in nature, in greater than natural abundance due to human activity. Which ultimately has a detrimental effect on the environment and therefrom on living organisms and mankind. For example lead, mercury, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide. Etc.
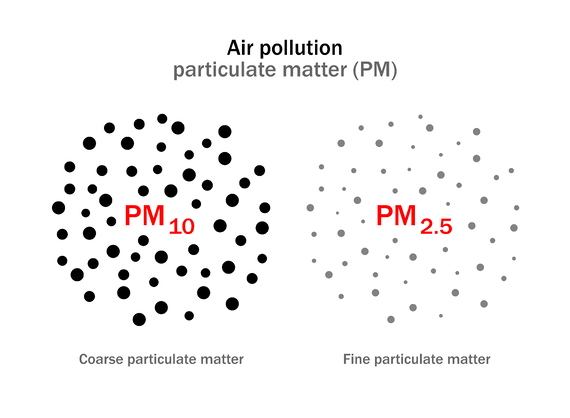
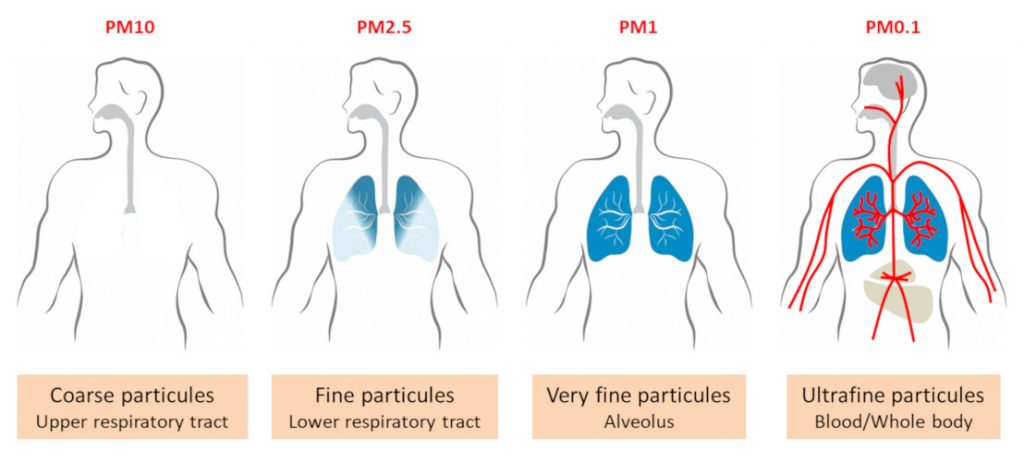
Air pollution due to particulate matter
Thus, small solid particles and liquid droplets are collectively called as particulates. Particulates are present in the atmosphere in fairly large numbers and pose a serious air pollution. They are classified, in accordance with particle size and nature, into different types such as fumes, dust, ash, carbon, smoke, lead, asbestos, mist, spray, oil, grease etc.
Formation of Particulate Pollutants
Natural Formation
Natural processes like volcanic eruptions, wind and dust storms, salt spray etc., release particulates into the atmosphere. Nearly 2000 million tonnes of particulate matter is entering into the atmosphere from natural resources per every one year.
Man-Made Particulate Pollutants
Manmade activities also inject 450 million tonnes of particulates into the atmosphere which causes air pollution. Dust and asbestos type of particulate pollutants enters into the atmosphere during the construction. Similarly fly ash from power plants, smelters, mining processes and smoke due to the incomplete (or) partial combustion of fuel etc., are also man made sources for particulate pollutants.
Particulate pollutants may be classified according to their nature and sizes, as follows:
Dust :
Dust is formed by solid particles and their size range from I micron to 100 microns. Dust particles with a size of 0. 1 micron are also present in the atmosphere. Dust panicles are:
- Entrained by gases directly from the materials being handled or processed, E.g. coal
- The off-spring obtained directly from the parent material when it undergoes a mechanical operation. E.g . Saw-dust from works;
- Entrained materials used in mechanical operations, E.g. sand From sand blasting .
Fume :
The size of these particles are less than I micron. Fumes are generally formed from particles of the metals and metallic oxides. Fumes are formed by the condensation of vapors by sublimation, distillation, calcination and by other chemical processes and chemical reactions.
Spray :
Liquid particles obtained from the parent liquid by the mechanical disintegration processes such as atomization is known as Spray.
Smoke :
Smoke is a collection of tiny solid, liquid and gas particles. Although smoke can contain hundreds of different chemicals and fumes, visible smoke is mostly carbon (soot), tar, oils and ash.