Product Details
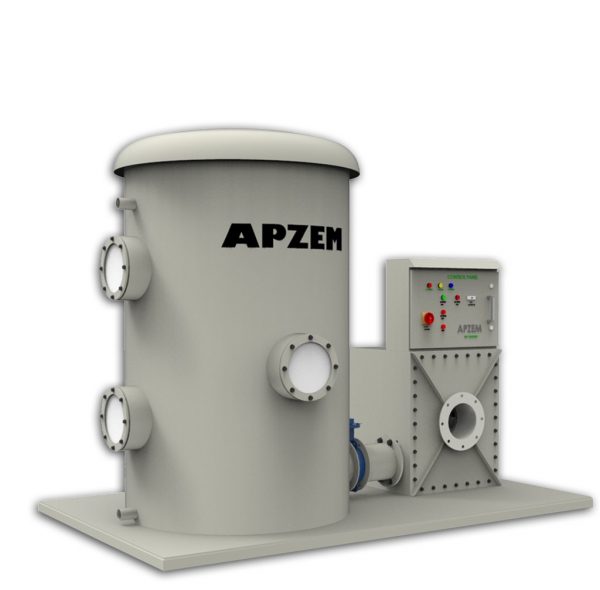
STP Scrubber
Odor Control System for Sewage Treatment Plan
STP Scrubber located near residential area creates issues if the STP Scrubber produces unpleasant odors. The odor control unit is becoming primary design consideration for wastewater treatment facilities. Areas in which most odor problems are collection system, primary treatment facilities and solid handling facilities. Generally, Odor Control System for Sewage Treatment Plant are produced by biological reaction at anaerobic/septic conditions.
Product Catalogue
Description
STP Scrubber
Odor Control System for Sewage Treatment Plant
STP ODOR CONTROL UNIT
STP Scrubber located near residential area creates issues if the STP produces unpleasant odors. The odor control unit is becoming primary design consideration for wastewater treatment facilities. Areas in which most Odour Control System for Sewage Treatment Plant, primary treatment facilities and solid handling facilities. Generally, odors are produced by biological reaction at anaerobic/septic conditions.
This condition occurs when oxygen transfer to the wastewater is limited. In the anaerobic state, the microbes present in the wastewater have no dissolved oxygen available for respiration. In the absence of dissolved oxygen (DO) and in the presence of soluble Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD), sulfate-reducing bacteria convert the sulfate ion to sulfide.
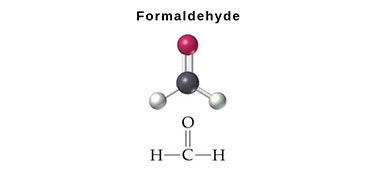
SO42- Organic matter H2S + CO2
Sulfur reducing bacteria, which uses sulfur as an energy source, are the primary producers of large quantities of H2S. Sulfur reducing bacteria live in oxygen deficient environment such as deep wells, plumping systems, etc. Due to its low solubility in wastewater, it is released into the atmosphere, producing an offensive odor. Chemical compounds associated with odor are Inorganic compounds, Mercaptans and Organic compounds containing Nitrogen and Sulfur atoms. Among these, Ammonia and Hydrogen sulphide are the main Odor Control System for Sewage Treatment Plant causing compounds.
Threshold limit of odor causing agents
| Name | Formula | Characteristic | Odor Threshold (ppm) |
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | Rotten eggs | 0.00047 |
| Ethyl mercaptan | CH3CH2-SH | Decayed Cabbage | 0.00019 |
| Methyl mercaptan | CH3-SH | Decayed Cabbage | 0.0011 |
| Dimethyl sulfide | CH3-S-CH3 | Decayed Vegetables | 0.0001 |
| Sulfur dioxide | SO2 | Pungent, Irritating | 0.009 |
| Benzyl mercaptan | C6H5CH2-SH | Putrid – Unpleasant | 0.00019 |
| Types | Working principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Wet scrubber | Process of absorption as well as chemical reaction to remove gases from contaminated gas streams | • Chemical costs at high flows
• High air flow capabilities • Versatility for various gases |
• High maintenance
• Fouling of packing surface • Cost of water addition • Disposal of caustic solution |
| Bio filter | Biofiltration uses the process of biological degradation to remove odorous gases from a contaminated air/gas stream. | • Low operating cost
• Applicable for high concentration of H2S |
• High maintenance
• Biofilters can handle some high concentrations of H2S (>200 ppm) • Large foot print |
| Dry scrubber | A product in which adsorbent is uniformly distributed and the pollutants is removed by physical adsorption | • No maintenance
• High efficiency |
• High media consumption
• Not regenerable |
| Engineered media dry scrubber | A product in which adsorbent is uniformly distributed and the pollutants is removed by both physical adsorption and catalytic/chemical conversion | • No maintenance
• Very high efficiency • High adsorption capacity for H2S • Regnerable • Low media |
• Not applicable for high concentration of H2S (for >200 ppm) |
- Removes odor from sewer exhaust by using physical adsorption and chemical conversion
- Adsorption is when ions, atoms, or molecules, from one source adhere to the surface of another element. Conversely, absorption is when the substrate incurs volume from the odorous substance.
- Adsorption uses activated carbon to act as the media. This is done by forcing the odorous air displaced from the wet well across a bed of activated carbon, which produces clean air.
- Class of activated carbon: Engineered activated carbon for sewage air
- Flow rate: Minimum of 6 x airspace/headspace volume per hour. If the volume of a SPS wet well at the lowest operating level is 10 m³, then the required minimum flow rate is 60 m³/hour.
- Outlet concentration as achieved at the outlet
- Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) = 0.1 ppm , Mercaptans (Thiols) = 0.02 ppm
- Otherwise, at a level that is demonstrated to achieve no odour nuisance at the nearest residence or public space.
Odor Control System for Sewage Treatment Plan
- Physical adsorption and catalytic conversion property
- It can typically remove 99.9% of all incoming contaminates.
- The bed life is defined as the length of time between replacements of the activated carbon media based on breakthrough of gas contaminants above the target design levels.
- Advantages: Very high efficiency, Regeneration of carbon. https://www.apzem.in/index.php/product/odor-control-system-for-sewage-treatment-plant/
Once the hydrogen sulfide concentration gets higher it is better to move onto a different type of odor control (i.e. bio-filtration or chemical scrubbing).