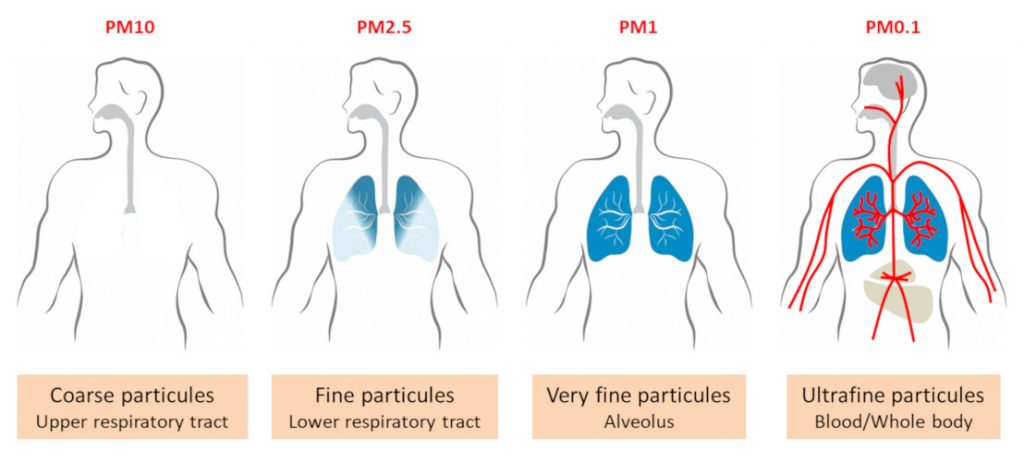
Particulate Pollutants
Pollutant is a substance present in nature, in greater than natural abundance due to human activity. Which ultimately has a detrimental effect on the environment and therefrom on living organisms and mankind. For example lead, mercury, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide. Etc.
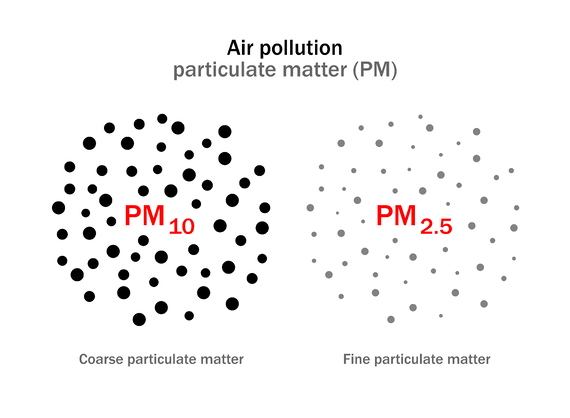
Air pollution due to particulate matter
Thus, small solid particles and liquid droplets are collectively called as particulates. Particulates are present in the atmosphere in fairly large numbers and pose a serious air pollution. They are classified, in accordance with particle size and nature, into different types such as fumes, dust, ash, carbon, smoke, lead, asbestos, mist, spray, oil, grease etc.
Formation of Particulate Pollutants
Natural Formation
Natural processes like volcanic eruptions, wind and dust storms, salt spray etc., release particulates into the atmosphere. Nearly 2000 million tonnes of particulate matter is entering into the atmosphere from natural resources per every one year.
Man-Made Particulate Pollutants
Manmade activities also inject 450 million tonnes of particulates into the atmosphere which causes air pollution. Dust and asbestos type of particulate pollutants enters into the atmosphere during the construction. Similarly fly ash from power plants, smelters, mining processes and smoke due to the incomplete (or) partial combustion of fuel etc., are also man made sources for particulate pollutants.
Particulate pollutants may be classified according to their nature and sizes, as follows:
Dust :
Dust is formed by solid particles and their size range from I micron to 100 microns. Dust particles with a size of 0. 1 micron are also present in the atmosphere. Dust panicles are:
- Entrained by gases directly from the materials being handled or processed, E.g. coal
- The off-spring obtained directly from the parent material when it undergoes a mechanical operation. E.g . Saw-dust from works;
- Entrained materials used in mechanical operations, E.g. sand From sand blasting .
Fume :
The size of these particles are less than I micron. Fumes are generally formed from particles of the metals and metallic oxides. Fumes are formed by the condensation of vapors by sublimation, distillation, calcination and by other chemical processes and chemical reactions.
Spray :
Liquid particles obtained from the parent liquid by the mechanical disintegration processes such as atomization is known as Spray.
Smoke :
Smoke is a collection of tiny solid, liquid and gas particles. Although smoke can contain hundreds of different chemicals and fumes, visible smoke is mostly carbon (soot), tar, oils and ash.
Secondary Pollutants
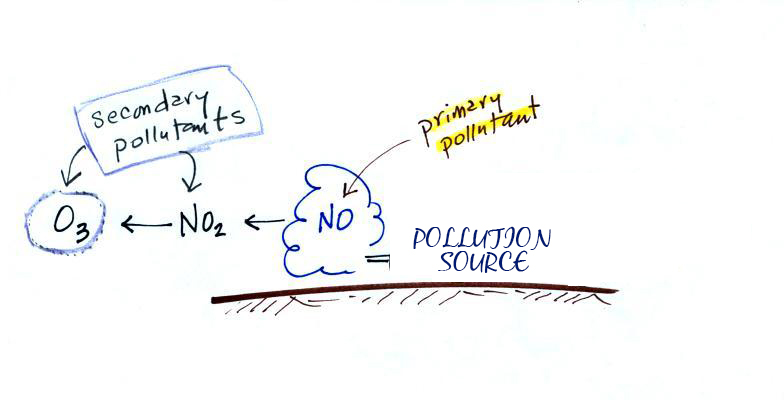
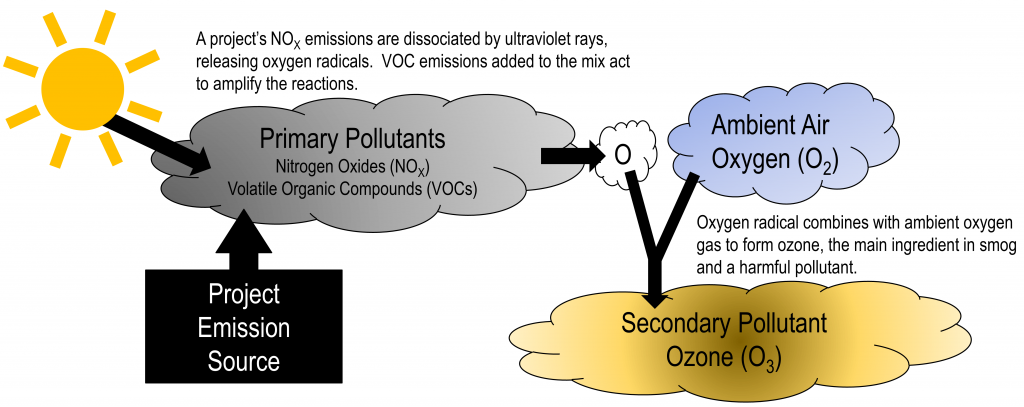
All the gaseous pollutants are primary pollutants. These pollutants are emitted directly and such are not found in the atmosphere. Instead, they form as a result of the pollutants emitted from these sources reacting with molecules in the atmosphere. Pollutants that are emitted into the environment from a source called Primary pollutants. There are also secondary pollutants which are formed in the atmosphere.
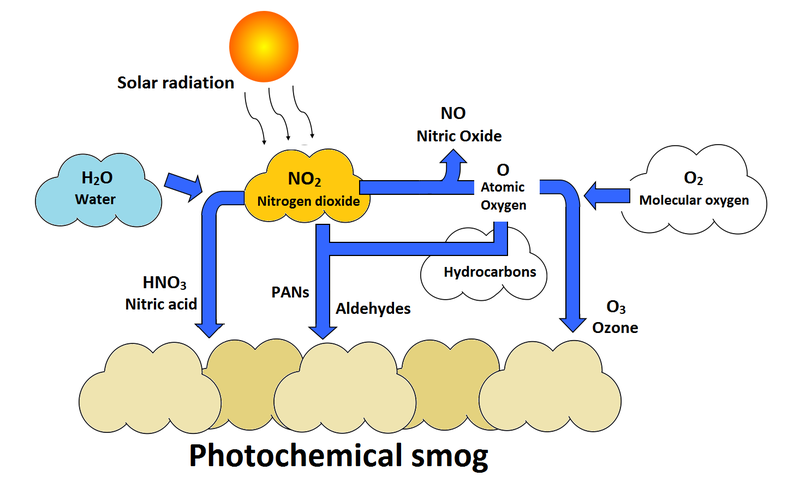
Secondary pollutants are those which are formed in the air due to interaction of primary air pollutants among themselves or by reaction with normal atmospheric constituents like sunlight, water vapor etc. With or without photo activation. For example ozone, formaldehyde, peroxy – acetyl nitrate and acidic mist like H2SO4 (SO2 + moisture), smog, photochemical smog.
Evidences and experiments indicate that exhaust gases of automobiles have particular importance in the formation of secondary pollutants For example
Nitrogen oxide produced in the combustion of petroleum and other fuels emitted to the atmosphere, yield ozone in the presence of sunlight. It is to be noted that ozone is not emitted as such to the atmosphere but formed only from primary pollutants by the interaction in the atmosphere and thus constitute of secondary pollutants. The ozone produced reacts with hydrocarbons to form a series of compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, organic acids, acyl nitrates and epoxy compounds. This types of photochemical reactions usually occur in smog. The term ‘ smog’ denotes a mixture of smoke and fog .it is reported that during a smog , the concentration of ozone and oxidant material are found to be high . According to the Haagen – smit theory , ultraviolent rays in the sunlight break the nitrogen dioxide molecule to form nitric oxide and atomic oxygen . These products react with molecular oxygen to form ozone. The reaction may be represented as follows
- NO2 – NO + O
- O2 + O – O3
- NO + O2 – NO3
- NO3 + O2 – NO2 + O3
- 2NO2 + O3 – N2O5 + O2
- NO + O3 – NO2 + O2
The liberated molecular oxygen reacts with molecules, of aldehydes and Oxy- genated organic compounds. which are activated by the absorption of light .
RCOOOH+O2 – RCOOH + O2
Thus once again ozone is liberated as a by product. On absorption of light energy, some of the aldehydes and ketones become free radicals. They react with molecular oxygen as follows
HCO + O2 – HCO3
The free radical HCO3, reacts further with molecular oxygen, nitric oxide and hydrocarbons as Follows
HCO3 + O2 – HCO2 + O3
HCO3 + NO – HCO2 + NO2
The cycle reaction is set in motion and numerous products are formed. It is to be noted that ozone and nitrogen dioxide are evolved continuously throughout the cycle of reaction. Free radicals lead to several other types of free radicals reaction and polymerization and oxidation chain reaction.
Though these reaction are studied well, the chemistry of photochemical smog is still not clearly understood. Many attempts have been made to reduce the level of ozone in the atmosphere. Actually, if the amount of hydrocarbons released in the atmosphere is reduced, then the ozone formed will be utilized in the oxidation of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide. But unfortunately the level of ozone have never decreased and the puzzle has not yet been solved .
Primary Pollutants

Outdoor air is filled with millions of particulate pollutants. Apzem provides the industry best experts who perform Air Quality Monitoring Services for Stack, Indoor & Ambient Environment .
Air is not clean in nature, because of natural and man- made pollution. Gases such as CO, SO2 and H2S are continuously released into the atmosphere through natural resources Ex: Volcanic activity, Vegetarian decay and forest fires. Air are distributed from the tiny particles of solids and liquids by wind, Volcanic explosion and other natural explosion.
The main sources of air pollutants are primary pollutants, Secondary pollutants, and Particulate Matter.
CARBON MONOOXIDE
Carbon monoxide is released into the atmosphere mainly from the automobile fume, smoke, and vapor. Next to carbon dioxide. Carbon monoxide is considered to be the most abundant pollutant and it may show wide diurnal variations in the urban atmosphere. Concentrations of carbon monoxide vary, depending upon the density of motor traffic. However. Carbon monoxide is usually present in amounts far below the threshold concentration in areas where traffic is less.
SULPHUR DI-OXIDE
Sulphurdioxide is one of the principal contaminants of air. Sulphur dioxide has its origin in the combustion of sulphur being fossil fuels. It is also present in appreciable quantities in air where coal is used as a fuel. Electric power plants. Sulphur dioxide is also released from smelters where sulphur as an ore is roasted e.g., in copper. Lead and Zinc smelting industries. Oil refineries. Sulphuric acid manufacturing industries. Fertilizer industries and paper and pulp industries give out significant amounts of sulphur di oxide Smelting operations are reported to cause heavy damage to agricultural and forest areas. Since sulphur di oxide is readily absorbed by water surfaces, soil and vegetation, deterioration and corrosion affect materials such as metals, paper, paints leather, textiles, cement, and other building material.
HYDROGEN & ORGANIC SULPHIDE
Sulphide causes odour nuisance when present even in very low concentration .However, there are not released in appreciable quantities by industrial operation since the effluents are treated before they are exposed to the atmosphere. Natural Gas refining manufactures of coke, manufacture of paper, distillation of tar and petroleum , manufacture of viscose rayon and some other chemical processes produce hydrogen sulphide.
HYDROGEN FLUORIDE
Hydrogen Fluoride and other volatile fluorides are considered to be serious pollutants even where present in concentration of 0.001 ppm by volume. Fluorides are liberated mainly from aluminum smelting industries Moreover, fluorides have the capacity to etch glass and can thee, cause considerable material destruction
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
The concentrations of hydrogen chloride in the atmosphere are found to be less. However, higher concentrations can cause damage to vegetation and also to properties.
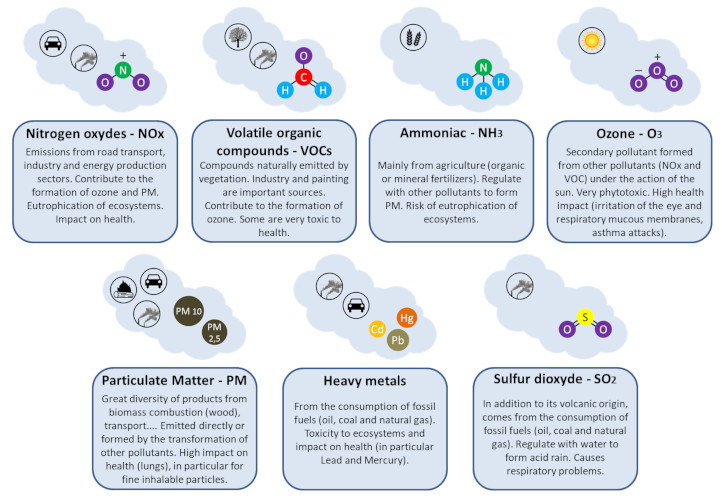
NITROGEN OXIDE
The primary, source of oxides of nitrogen is automobile exhaust. These are also produced as by product of some chemical industries such as manufacture of nitric acid, manufacture of sulphuric acids manufacture of nylon intermediates. It is reported that the products of combustion of natural, contain up to 50 ppm of nitrogen. The oxides of nitrogen are the second most abundant atmospheric pollutants. These are extremely dangerous to human health. The effects are sometimes more severe than carbon monoxide.
ALDEHYDE & ORGANIC ACID
These are present in lower concentrations in the atmosphere. The incomplete combustion of petroleum fuels and incomplete oxidation of lubricating oils from aldehydes and organic acids combustion of natural gas may also contribute to the formation of these materials.
Thermal Power Plant Pollution
Thermal Power Plant Pollution
Thermal power plants gives out lot of gas which are harmful to our environment. Thermal power plant is used to converts heat energy into electric power. Chief justice of India SA Bobde said on Friday (29.2.20), he wanted all the thermal plants in the country shut to prevent environmental pollution. Bobde was dealing with a case from Uttarakhand where many projects had come under the court scanner along with Justices BR Gavai and Surya Kant. Thermal pollution is the degradation of local environment, in particular the localized waterways, were changed by discharge of waste water from power plant.
Effect on Atmosphere
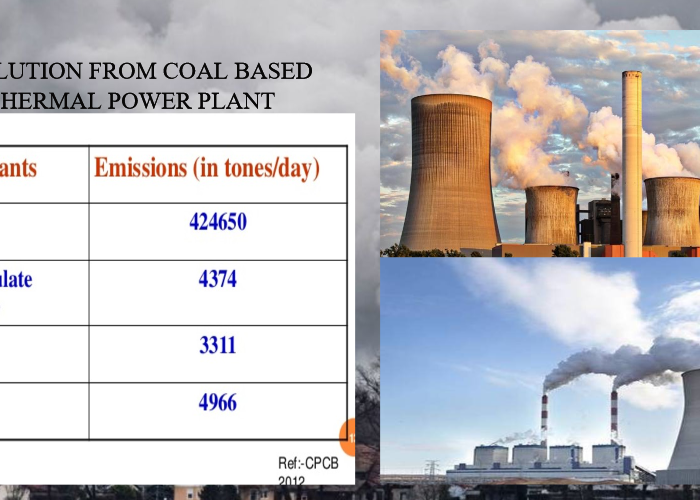
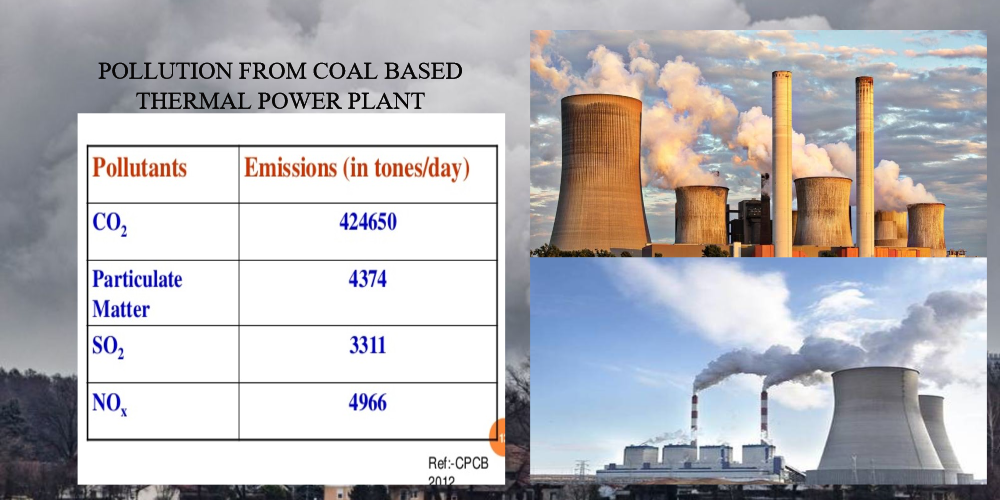
Thermal power plant produce lot of greenhouse gases, which are by-products of burning fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide is one of the main gas that is released from burning of fossil fuels and it is the main reason for global warming. Thermal power plant is one of the reason to increase the carbon dioxide level throughout the world. Sulfur dioxide is another gas released from power plants. It is not a greenhouse gas, it gave indirect effects to atmosphere because it affect the scattering of sunlight. So it is considered as indirect greenhouse gas. This will return to earth as acid rain and will impact on ecosystem. The level of sulfur dioxide released from thermal power plants depend on the amount of sulfur dioxide released from thermal power plants depends on the amount of sulfur in the coal. The coal used in thermal power plant has an average between 0.1 and 3.5% of sulfur and the thermal power plants are the largest emitters of sulfur dioxide worldwide.
Nitrogen oxide are another gases that released in thermal power plants. It is one of the largest contributor to global nitrogen oxide levels. Both nitrous oxide and nitrogen oxides are not greenhouse gases, but it has an indirect effect on the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxide will cause respiratory issues and they combine with other atmospheric gases and moisture to form acid rain and smog. The other big pollutant to atmosphere is ash in the thermal Plants. Coal is used in thermal power generation which produce fine particles of ash will cause environmental problem. Ash will spread in the atmosphere will contains ash particles like silica, alumina, iron oxide, calcium, magnesium, lead, arsenic, cobalt and copper. Ash contain particulate matter known as PM2.5, are the particles less in diameter.
Effect on Local Environment
Thermal pollution is one the biggest problem in local environment. When the water in power plant is no longer usable, it gets discharged into local waterway. Wastewater generally have high temperature than local natural water, it can increase the temperature of water and it also have negative impact on local ecosystem. The released ash particles contain metal ions which can escape into local ecosystem and it also contain radioactive nuclides. Radioactive nuclides that emit radiation as they undergo radioactive decay through emission of alpha, beta or gamma particles. They affect the local environment from waterways, soil, vegetation and other living organisms.
Wildfire and climatic change
Wildfire and climatic change
Wildfire plays a major role in the forest ecosystem. But wild fire had many environmental related benefits like they can cut back the sick or dead trees and let the trees to re-grow for later. This proves that fire not destroy but also give re-growth to the tress in the forest. Wildfires are unpredictable and unplanned fires occur in the forest. Wildfires are burn at a temperature more than 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature is twice hot as the surface of Venus. It will also spread faster at the ground, twice the human can run. There must be three things present, like oxygen, heat and fuel, a fire will start. This can be called as a fire triangle by foresters. If there is any plenty of these elements, the fire will spread towards the direction. To control the fire, we should limit any one of these in the three elements.
Effects of Wildfires
Plant purifies the atmospheric air by taking carbon dioxides and impurity air and release oxygen. When plant life is extinguished by fires, the quality of air that we breathe will dismiss and greenhouse gas will increase in the atmosphere will lead to change in climate and global warming. The clouds of huge smoke by wildfires will lead to air pollution. If the greenhouse gas will increase it will lead to global warming and the smoke and dust which destroy will cause air pollution.
We all know that forest soils are loaded with nutrients arise from decaying of remaining forest. There are some numerous natural features in the forest soil. While the burning of trees and leaves, the soil expose to make it readily unsafe to soil erosion. The entire value of the soil destroys due to high temperature caused by wildfires.
In dry tropical forest the commonly happen major issue was forest fire. During the forest fire, thousands of acres of trees are removed. Every year, during forest fire are shows that the quality of forest features like soil fertility, biodiversity and ecosystem will reduced.
The smoke from wildfires are mostly water vapour, also it contains gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide and other particulate matter which affect human health.
Causes of Wildfire
90% of wildfires may cause by humans. A worldwide study of smoking related fire by epidemiologists says that the smoking is the cause of fire. The effect and dust also cause breathing trouble and will lead to respiratory disorders. Due to climatic change, since 2000, an average of 72,400 wildfires had burned an average of 7.0 million acres.
In the earth’s crusts is usually discharges hot magma which releases lava during volcanic eruption. Magma is a molten rock found below the earth surface.
Wildfires have both immediate and long-term effects on air quality. Large amount of smoke released in the atmosphere during wildfire. The fire during air pollution may travel to a greater distance and it may affect the human health. It makes difficult to breathe when we are inhaling the polluted air.
Wildfire will affect local atmospheric pollution, and release carbon in the form of carbon dioxide. The ash and smoke generated during wildfires will pollute the atmosphere and affect the human health issue while people breathe the polluted gas. The health issues like breathing problems, eye irritation and respiratory disease are the common heath issue while people live near the fire areas.