Author: Page Editor
Transport Air Pollution
Transport Air Pollution
Vehicular pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment by motor vehicles. These are the materials, known as pollutants, have several bad effects on human health and the ecosystem.
Air pollution is caused by the solid and liquid particles and certain gases that are suspended in the air. These particles and gases can be come from car and truck exhaust, factories, dust, pollen, mold spores, volcanoes and wildfires. The solid and liquid particles suspended in our air is called aerosols.
Environmental Effects of Transport
The environmental effects of transport are significant because transport is a major user of energy, and burns most of the world’s petroleum. This creates of air pollution, including nitrous oxides and particulates, and is a significant contributor to global warming through the emission of carbon dioxide.

Transport Air Pollution
Admittedly, the air transport is extremely polluting but so are cars. Air traffic represents less than 2-3% of the global CO2 emissions whereas road traffic accounts for around 10% of these direct emissions. Still, plane remains among the most polluting means of transport, together with cars.
The movements of pollutants in the atmosphere is caused by transport, dispersion, and deposition. Transport are movement caused by a time averaged wind flows. Dispersion results from the local turbulence, that is, motions that last less than the time used to average the transport.
Transport Air Pollution
Transport also leads to releases of pollutants, which can be spread beyond the reach of transport networks. They can be contributing to background concentrations of particulate matter, ozone and nitrogen dioxide, affecting people, plants and animals.
The transportation sector generates the largest share of greenhouse gas emissions. Greenhouse gas emissions from transportation primarily comes from burning fossil fuel for our cars, trucks, ships, trains, and planes.
Passenger vehicles are the major pollution contributor, producing significant amounts of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and other pollution. In 2013, transportation contributed more than half of the carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, and almost a quarter of the hydrocarbons emitted into our air.
Rail transportation emits about 0.2 pounds of greenhouse gases per passenger mile (55 g/km) when each car is filled with 50 passengers
Reduce Pollution from Vehicles and Engines
- Drive less.
- Drive wise.
- Choose fuel efficient vehicles.
- Don’t idle.
- Optimize home deliveries.
- Use efficient lawn and gardening equipment.
Effects of Transport Air Pollution
Vehicle emissions contribute to the formation of ground level ozone (smog), which can be trigger health problems such as an aggravated asthma, reduced lung capacity, and increased susceptibility to respiratory illnesses, including pneumonia and bronchitis.
Total emissions are generally a function of the emission factors of each transport mode than their level of activity, which has implied a variety of impacts on the environment. These impacts fall within three categories,
-
Direct impacts:
The immediate consequences of transport activities on the environment where the cause and effect relationship are generally clear and well understood. For instance, noise and carbon monoxide emissions are known to have a direct harmful effects.
-
Indirect impacts:
The secondary effects of transport activities on environmental systems. They are often to the higher consequence than direct impacts, but the involved relationships are often misunderstood and more challenging to establish. For instance, particulates, which are mostly the outcome of incomplete combustion in an internal combustion engine, are indirectly linked with a respiratory and cardiovascular problems since they contribute, among other factors, to such a conditions.
-
Cumulative impacts:
The additive, multiplicative or synergetic consequences of transport activities. They consider as the varied effects of direct and indirect impacts on an ecosystem, which are often unpredictable. Climate changes, with complex causes and consequences, is the cumulative impact of several natural and anthropogenic factors, in which transportation plays a role. The shares of transportation in global, CO2 emissions is increasing. 22% of global CO2 emissions are attributed to the transport sectors, with this share is around 25% for advanced economies such as the United States.
https://www.apzem.com/india/products/product-categories.html
TRESS to Reduce Air Pollution
TRESS to Reduce Air Pollution
The biggest problem of the human being is how to reduce air pollution. Trees are act as the earth’s purification system by absorbing airborne chemicals and releasing oxygen. To tackle global air pollution, we need to halt deforestation & plant billions of trees.
 Tress to reduce Air Pollution
Tress to reduce Air Pollution
Industrial human activities, such as a burning of greenhouse gases, release toxic chemicals and particles into the air. Concentrations are worse in crowded urban areas, and countries with huge manufacturing industries such as China, India and Bangladesh have the highest recorded levels of globally.
TRESS to Reduce Air Pollution
Air pollution is also causes acid rain, which in turn damages trees and turns soil and waterways acidic. Higher levels of black carbon and ground-level ozone can be harm crop yields, worsening famine and poverty.
WHO Report
According to the World Health Organization report, nine out of ten people breathe polluted air. Approximately seven million deaths every year are attributed to bad air quality, which increases the risk of strokes, lung cancer & heart disease. Breathing a dirty air has been also being linked to immune system damage, as the body becomes inflamed to try and fight off the particles it is being exposed to.
Emissions from the vehicles has also contributed to poor air quality. In developing countries, deforestation and burning of charcoal and wood for fuel is a driving factor. Cutting down trees are not only releases CO2, but also prevents forests from purifying our air.
Many governments have the air pollution index and have set targets for ‘safe’ levels of air pollution, but almost every country is currently exceeding dangerous levels.
Benefits of Tress
Trees are absorbing the toxic chemicals through their stomata, or ‘pores’, effectively filtering these chemicals from the air. Trees also mitigate the greenhouse gas effect by trapping heat, reduce the ground-level ozone levels and release life-giving oxygen.
Trees has come in many shapes and sizes, and each is suited for different conditions. Think about where you will plant the tree and what your preference is for its full grown size and shape.
Tress Suitable for Controlling Dust Pollution
- Common Ash
- Little leaf linden
- Norway maple
- Turkey oak
- Ginkgo
- Large leaf linden
- Oak Tree
Trees have improved the air quality in direct and indirect ways. Indirectly, Tress Can help by shading surfaces and reducing temperatures. In buildings are shaded by trees, it reduces the need for conventional air conditioning, and the emissions of greenhouse gases that comes with it. Plus, the lower temperature has decrease the risk of harmful pollutants like ground level ozone that commonly spike on hot days in urban areas.
Uses of Trees
- Trees provide food
- Trees protect the land
- Trees help us breathe
- Trees provide shelter and shade
- Trees are a natural playground
- Trees encourage biodiversity
- Trees provide sustainable wood
- Trees conserve water
Trees are the pillars of sustaining life on earth. Trees consume carbon dioxide and, by photosynthesis, then emit oxygen. By holding the soil to its roots, can also assists in reducing soil erosion. Trees absorb atmospheric carbon and store it in their wood and bark, this is slowing the rate of global warming.
TRESS : Reduce the effects of climate change
Trees absorb carbon dioxide (CO2), and removing & storing the carbon while releasing the oxygen back into the air.
During one year, a mature tree is absorbing more than 48 pounds of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen in exchange.
While they emit a volatile organic gas, trees take up a variety of air pollutants, including both the ozone and nitrogen oxides, which reduces the ambient concentrations that we breathe.
https://www.apzem.com/india/products/product-categories.html
Global Warming – Effects, Prevention, An Over View
Global warming
Global warming is occurring when carbon dioxide (CO2) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight or solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface. Normally this radiation would escape into the space, but these pollutants, which can be last for years to the centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter. These heat-trapping pollutants specifically carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and synthetic fluorinated gases are known as greenhouse gases, and their impact is called the Greenhouse Effects. Global Warming is the rise in average temperatures of across the globe, which has been ongoing at least since record keeping began in 1880.
Although people tend to use these terms interchangeably, global warming is just one aspect of climate changes. “Global warming” refers to the rise in global temperatures due to mainly, the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
One of the most dramatic effects of the global warming is the reduction in Arctic sea ice. Sea ice hit records-low extents in both the fall and winter of 2015 and 2016, meaning that at the time when the ice is supposed to be at its peak, it was lagging. The melt means there is less thick sea ice that persists for multiple years. That means the less heat is reflected back into the atmosphere, by the shiny surface of the ice and more is absorbed by the comparatively darker ocean, creating a feedback loop that causes even more melt, according to NASA’s Ice Bridges.
Impacts of Global Warming
Each year scientists learn more about the Consequence of Global Warming, and each year we also gain new evidence of its devastating impact on people and the planet. As the heat waves, droughts, and floods associated with climate change become more frequent and more intense, communities suffer and death tolls rise. Normally the radiations would escape into space, but these pollutants, which can last for years to the centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter.
Other Effects of Global Warming
- Disappearing Glacier, early snowmelt, and severe droughts will cause more dramatic water shortages and continue to increase the risk of wildfires in the American West.
- Rising Sea Level will lead to even more coastal flooding on the Eastern Seaboard, especially in Florida, and in other areas such as the Gulf of Mexico.
- Forests, farms, and cities will face troublesome new posts, heat waves, heavy downpours, and increased flooding. All of these can damage or destroy agriculture and fisheries.
- Disruption of habitats such as coral reefs and alpine meadows could drive many plant and animal species to extinction.
- Allergies, asthma, and infectious disease outbreaks will become more common due to increase the growth of pollen-producing ragweed, higher levels of air pollution, and the spread of conditions favorable to pathogens and mosquitoes.
Causes of Global Warming
- Oil and Gas – Oil and Gas is used all the time in almost every industry.
- Deforestation. Deforestation is the clearance of woodland and forest-this is either done for the wood.
- Power Plants
- Oil Drilling
- Transport and Vehicles
- Consumerism
Prevention
- Limiting the amounts of energy in your home by using energy efficient light bulbs and appliances, and knowing how to use the appliances properly.
- Use an air conditioner and heater only when necessary, and make sure your house is properly insulated.
- Use a hot water sparingly and use cold water when washing clothes and dishes.
- Reduce the driving and use other means of transportation like walking, biking or carpooling.
- Recycle and use reusable bags for purchases and use the refillable water bottles.
Clean Our Air
Clean Our Air
Since air pollution is damaging to the environment and human health, we all need to play our part in reducing the level of air pollution in our neighborhoods.
The scientific evidences of disturbing links between the air pollution and health continues to build. In accordance with recent WHO estimates, exposure to the air pollution is the more important risk factors for major non-communicable diseases than previously thought. Air pollution is the largest contributor to the burden of disease from the environment. Air pollution can cause and exacerbates a number of diseases, ranging from asthma to cancer, pulmonary illnesses and heart disease.
Clean Air Act
Experience with the Clean Air Act since 1970 has been that protecting public health and building the economy can go hand in hand. Clean Air Act programs have lowered levels of six common pollutants — particles, ozone, lead, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide — as well as numerous toxic pollutants.
Air quality improvements has enabled many areas of the country to meet national air quality standards set to protect public health and the environment.
State emission control measures to implement the Act, as well as EPA’s national emissions standards, have contributed to air quality improvements.
Air pollution and the Environment
Increased ground-level ozone also causes damage to cell mem – branes on plants, inhibiting key processes required for growth and development. The loss of plant cover affects us all. Trees and other vegetation absorb pollutants such as excessive nitrogen dioxide, ozone and the particulate matter, through their leaves and needles and thereby help improve air quality. Less plant cover, this means less filtering capacity to clean our air.
Environmental damage
Lower air pollution level mean less damage to the health of ecosystems. Environmental effects of air pollution includes damage to plants and long-term forest health, soil nutrients deterioration, accumulation of toxics in the food chain, damage to fish and other aquatic life in lakes and streams, and nitrogen enrichment of coastal estuaries causing oxygen depletion and resulting harm to fish and other aquatic animal populations.
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and ultra-low NOx burners for NOx emission
- Scrubbers which achieve 95 percent and even greater SO2 control on boilers
When you breathe, very small particles — such as dust, soot, and acid droplets — can slip past your lung’s natural defense system. These particles get a stuck deep in your lungs and may cause problems more asthma attacks, bronchitis and other lung diseases, decreased resistance to infections, and even premature death for the elderly. Here the few things you can do to reduce particulate matter pollution and protect yourself.
Prevention Step
- Do not use your wood stove or fireplace on days with unhealthy air.
- Avoid using leaf blowers and other types of equipment that raise a lot of dust. Use a rake or broom instead.
- Drive slowly on roads.
- Drive less, particularly on days with unhealthy air.
- Avoid vigorous physical activity on days with unhealthy air.
Take a strategic approach, we must think big and act boldly, but we recognize that the progress comes one step at a time. Our focus is only on making a difference in public policy and in our lives and our environment, not just making a statements.
Clean Our Air – At Home
- Use an energy efficient appliance.
- Turn off appliances when not in use.
- Recycling waste and old equipment.
On the Move
- When you do not have to drive, walk, use public transport or cycle.
- Take a part in a car-sharing arrangement especially during peak traffic time.
- Avoid revving, acceleration gradually and use cruise control when on the motorway.
- Invest if you can in less polluting vehicles. https://www.apzem.com/india/products/product-categories.html
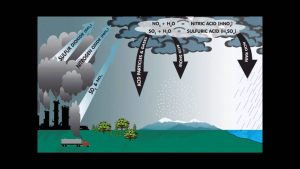
Acid Rain
Acid Rain: Acid rain is a results of air pollution. When any type of fuel is burnt, lots of different chemicals are produced. The smoke that comes from a fire or the fumes that come out of a car exhaust don’t just contain the sooty grey particles that you can be see – they also contain lots of invisible gases that can be even more harmful to our environmental.
Acid rain, or acid deposition, is a broad term that includes any form of precipitations with acidic components, such as sulfuric or nitric acid that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. This can be including rain, snow, fog, hail or even dust that is acidic.
https://www.apzem.in/index.php/product-category/fume-extractor/
https://www.apzem.in/index.php/product-category/dust-collector/
https://www.apzem.in/index.php/product-category/scrubber/
Acid rain is caused by the emissions of Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Some governments have made efforts since the 1970s to reduce the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide into the atmosphere. These efforts had positive results due to the widespread research on acid rain starting in the 1960s and the publicized information on its harmful effects.
Acidity and alkalinity are measured using the pH scale. 7.0 is neutral. The lower a substance’s pH (less than 7), the more acidic. It is the higher a substance’s pH (greater than 7), the more alkaline it is. Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6. It is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves into it forming weak carbonic acid. Acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
The Effects of Acid Rain
Acid rain can be carried great distances in the atmosphere, not just between countries but also from the continent to continent. The acid can be take the form of snow, mists and dry dusts. The rain sometimes falls many miles from the source of pollution but wherever it falls it can be having a serious effect on soil, trees, buildings and water.
Forests and all over the world are dying, fishes are dying. In Scandinavia there are dead lakes, which are the crystal clear and contain no living creatures or plant life.
Acid Rain proposes a very harmful effect on the ecosystems as well. The acidity in the water can cause many fish and sea life to die, and that can be throw off the whole food-chain. A test was done by the results, which were published in 1990, showed that most of the lakes in Adirondack area had low pH levels and that the lakes with these low levels had no fish.
Human health effects
Acid rain does not directly affect human health. The acid in the rainwater is too dilute to have the direct adverse effects. The particulates responsible for the acid rain (sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) do have an adverse effect. Increased the amounts of fine particulate matter in the air contribute to heart and lung problems, including asthma and bronchitis.
FOREST
- dissolve and wash away the nutrients and minerals in the soil
- cause the release of harmful substances such as aluminum into the soil.
- wear away the waxy protective coating of leaves, damaging them preventing them from being able to photosynthesis properly.
Reduce emissions
- Burning of fossil fuels is still one of the cheapest ways to produce an electricity so people are now researching new ways to burn fuel which don’t produced so much pollution.
- Governments have need to spend a more money on pollution control even if it does mean an increase in the price of electricity.
- Sulphur can be also ‘washed’ out of smoke by spraying a mixture of water and powdered limestone into the smokestack.
- Cars are now fitted with catalytic converters which remove three dangerous chemicals from the exhaust gases.