Author: admin
Clearing the Air: The Hazards of Welding Fumes and How to Stay Safe
Welding is a common industrial process used to join metal parts together. Although it is a highly efficient process, it also produces welding fumes that can be harmful to human health. Welding fumes are a mixture of metal oxides, gases, and vapors that can be inhaled by welders and other workers in the vicinity. In this blog, we will discuss the dangers of welding fumes and ways to prevent exposure.
Dangers of Welding Fumes:
Welding fumes contain several hazardous substances, such as manganese, lead, nickel, chromium, and cadmium, which can cause both short-term and long-term health effects. Short-term effects can include eye, nose, and throat irritation, dizziness, and nausea. Long-term exposure can lead to more serious health issues such as respiratory problems, lung cancer, and neurological damage.
Preventing Exposure to Welding Fumes:
Welding is a crucial process that involves joining two or more pieces of metal together by heating them to high temperatures. However, the process also produces a lot of hazardous fumes and gases, which can be harmful to the welder’s health. That’s why it’s important to use a welding fume extractor to remove harmful fumes from the air.
A welding fume extractor is a device designed to remove fumes and particles generated during welding, cutting, and grinding operations. It captures and filters the contaminated air, returning clean air into the work environment. Welding fume extractors come in various sizes, shapes, and configurations, and are designed to meet different types of welding applications.
One of the benefits of using a welding fume extractor is that it protects welders from the harmful effects of welding fumes. These fumes can cause serious health problems such as lung cancer, respiratory diseases, and other occupational illnesses. By removing these fumes, the extractor helps to create a safe and healthy work environment for the welder.
Another benefit of using a welding fume extractor is that it improves the quality of the weld. Welding fumes can affect the quality of the weld by depositing contaminants on the surface of the metal. This can lead to weaker welds and increased porosity. By removing the fumes, the welding fume extractor helps to ensure a clean, high-quality weld.
When choosing a welding fume extractor, it’s important to consider the type of welding being done, the size of the work area, and the type of filter needed. Some extractors use disposable filters, while others use reusable filters that can be cleaned and reused. The size of the extractor should be appropriate for the size of the work area to ensure that all fumes are captured and filtered.
A welding fume extractor is an essential tool for any welding operation. It helps to protect the welder’s health and ensures a clean, high-quality weld. When choosing an extractor, it’s important to consider the type of welding being done, the size of the work area, and the type of filter needed. By using a welding fume extractor, welders can work safely and efficiently without inhaling harmful fumes.
The Costly Cloud: How Air Pollution Impacts the Economy
Air pollution, the silent assailant lurking in our atmosphere, poses a grave threat to both public health and the economy. While the immediate impact on human well-being is evident, the long-term repercussions on economic stability and growth are equally concerning. In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted ways in which air pollution adversely affects the economy, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive action.
Health Costs:
One of the most direct and tangible consequences of air pollution is its detrimental effect on public health. Exposure to harmful pollutants leads to respiratory ailments, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature deaths. As healthcare systems struggle to cope with the increased demand for medical assistance, the accompanying costs skyrocket. These mounting healthcare expenses put a strain on public budgets, leaving less room for investment in vital sectors such as education and infrastructure.
Reduced Labor Productivity:
Unhealthy air quality takes a toll on workforce productivity, thereby hindering economic growth. Employees exposed to high levels of pollutants are more likely to suffer from respiratory problems and allergies, leading to increased absenteeism and decreased productivity. Moreover, studies have shown that air pollution can impair cognitive abilities, diminishing decision-making skills, and overall efficiency. This decline in labor productivity dampens economic output and competitiveness, adversely affecting both businesses and national economies.
Agricultural Productivity:
The impact of air pollution extends far beyond urban centers. Pollutants such as ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter harm crops, forests, and ecosystems. Reduced agricultural productivity not only leads to lower yields and food shortages but also causes price hikes in the market. Farmers bear the brunt of this, facing economic losses while trying to adapt to changing environmental conditions. Furthermore, the ripple effects of diminished agricultural output affect food processing industries, leading to job losses and economic instability in rural areas.
Tourism and Recreation Decline:
Clear skies and fresh air are often key factors that attract tourists to a destination. However, areas plagued by air pollution suffer a decline in tourism and recreational activities. Visitors are discouraged from exploring regions with poor air quality, impacting revenue streams for hotels, restaurants, and local businesses. Moreover, outdoor recreational activities, such as hiking, biking, or enjoying parks, become less appealing, leading to a decline in associated industries. The resulting economic downturn further exacerbates the negative cycle of air pollution’s impact.
Environmental Damage and Cleanup Costs:
Air pollution contributes to environmental degradation, including acid rain, smog, and the deterioration of ecosystems. Cleaning up polluted areas, restoring damaged environments, and implementing effective pollution control measures all incur substantial costs. Governments and communities must allocate resources to combat environmental damage caused by air pollution, diverting funds that could be used for infrastructure development or education initiatives.
Regulation and Compliance Costs:
Governments worldwide impose regulations and standards to curb air pollution, requiring industries to invest in pollution control technologies and adjust their production processes. Compliance with these regulations involves significant costs, including the installation of emission control equipment, continuous monitoring systems, and operational changes. While these measures are essential for public health and environmental preservation, the associated expenses impact business profitability and economic growth.
Reputation and Investment:
Regions marred by high levels of air pollution suffer from a tarnished reputation, deterring potential investors. Businesses may hesitate to establish operations in polluted areas due to concerns over employee health, reduced productivity, and negative public perception. The subsequent decline in investment opportunities limits job creation and economic growth in these regions, perpetuating a vicious cycle of stagnation.
Tackling Air Pollution for Sustainable Prosperity:
Air pollution, often underestimated as a mere environmental issue, poses significant threats to the economy. The detrimental effects on public health, labor productivity, agricultural output, tourism, energy consumption, environmental integrity, and investment opportunities underscore the urgency of combatting this invisible menace. Policymakers, businesses, and individuals must prioritize sustainable practices, embrace cleaner technologies, and implement stringent pollution control measures to safeguard public health, enhance productivity, and foster long-term economic prosperity. Only by addressing air pollution comprehensively can we create a healthier, more sustainable future for generations to come.
Clearing the Air: How Wet Scrubbers Neutralize Ammonia Gas
Ammonia is a versatile chemical compound widely used in various industries, including agriculture, refrigeration, and manufacturing. However, its presence in the air can be problematic, leading to health hazards, environmental pollution, and corrosion. This blog explores the hindrance of ammonia in industries and sheds light on how wet scrubbers neutralize ammonia gas, mitigating its adverse effects.
The Hindrance of Ammonia in Industries
Health Risks: Ammonia gas can cause severe health problems when inhaled, such as eye and throat irritation, respiratory issues, and even chemical burns. Workers in industries that handle ammonia, such as fertilizer production plants, refrigeration facilities, and chemical manufacturing units, are particularly at risk. Furthermore, accidental ammonia leaks can affect nearby communities, posing a threat to public health.
Environmental Impact: Ammonia emissions contribute to environmental pollution. When released into the atmosphere, ammonia can react with other pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, to form particulate matter and ground-level ozone, contributing to smog formation. Ammonia deposition can also disrupt ecosystems and lead to water pollution, harming aquatic life.
Corrosion and Infrastructure Damage: Ammonia is corrosive to many materials, including metals and concrete. In industries where ammonia is present, equipment, pipelines, and structures can suffer damage over time. This corrosion not only compromises the integrity of industrial infrastructure but also increases maintenance costs and reduces operational efficiency.
The Role of Wet Scrubbers in Neutralizing Ammonia Gas
Wet scrubbers are an effective pollution control technology widely employed in industries to reduce harmful emissions. These devices utilize liquid solutions or slurries to remove pollutants from gas streams. When it comes to neutralizing ammonia gas, wet scrubbers offer several advantages:
Absorption: Wet scrubbers use a liquid medium, typically water or a chemical solution, to absorb and dissolve ammonia gas. As the gas passes through the scrubber, it comes into contact with the liquid, which facilitates the transfer of ammonia from the gas phase to the liquid phase.
Chemical Reactions: In some wet scrubbers, the liquid medium contains chemical agents, such as acids or alkalis that react with ammonia to form harmless compounds. For example, in an alkaline wet scrubber, the ammonia reacts with an alkaline solution to produce ammonium hydroxide, which is less hazardous and can be safely disposed of or further processed.
Particulate Removal: Wet scrubbers can also remove particulate matter associated with ammonia emissions. By using a combination of liquid droplets and collection mechanisms, such as impaction or diffusion, wet scrubbers capture both gaseous ammonia and solid particles, effectively reducing emissions.
Benefits of Wet Scrubbers in Ammonia Control
Improved Air Quality: Wet scrubbers significantly reduce ammonia emissions, minimizing the risks to human health and improving air quality in and around industrial facilities. By neutralizing ammonia gas, wet scrubbers play a crucial role in maintaining a safe and healthy work environment.
Environmental Protection: The implementation of wet scrubbers aids in reducing ammonia’s environmental impact. By capturing and neutralizing ammonia emissions, these devices prevent the formation of harmful secondary pollutants, such as particulate matter and ground-level ozone. They also help in curbing ammonia deposition and its subsequent impact on ecosystems and water bodies.
Infrastructure Protection and Cost Savings: Wet scrubbers minimize corrosion caused by ammonia gas, extending the lifespan of industrial infrastructure and reducing maintenance expenses. By preventing damage to equipment and structures, industries can operate more efficiently and avoid costly repairs and replacements. The hindrance posed by ammonia gas in industries is a significant concern due to its health risks, environmental impact, and infrastructure damage. Wet scrubbers offer an effective solution by neutralizing ammonia emissions and capturing harmful particles. Implementing wet scrubbers not only protects workers’ health and improves air quality but also safeguards the environment and preserves valuable industrial infrastructure. As industries strive for sustainable and responsible operations, wet scrubbers play a vital role in mitigating the adverse effects of ammonia gas, fostering a safer and cleaner future.
Shielding Pharmaceutical Excellence and Safety
Introduction:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is a complex and highly regulated industry that plays a vital role in healthcare. However, one often overlooked aspect of this industry is pharmaceutical dust. Dust particles generated during the manufacturing process can pose serious risks to both product quality and the health and safety of workers. That’s where dust collectors step in as unsung heroes, effectively mitigating these risks and offering numerous benefits to the pharmaceutical industry.
The Dangers of Pharmaceutical Dust:
Pharmaceutical dust consists of fine particles that are generated during various manufacturing activities, such as milling, blending, and granulation. These particles can be hazardous in several ways:
Health Risks: Inhalation of pharmaceutical dust can be harmful to workers, potentially leading to respiratory issues, allergic reactions, and even long-term health problems. Protecting employees from exposure to airborne particles is crucial to ensure their well-being.
The Role of Dust Collectors: Dust collectors are specifically designed to capture and remove airborne dust particles. These devices are integral to maintaining clean and safe environments in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities.
Enhanced Product Quality: By efficiently removing dust particles, dust collectors minimize the risk of product contamination. This ensures pharmaceutical products’ integrity, purity, and consistency, meeting regulatory requirements and safeguarding patient safety.
Improved Workplace Safety: Dust collectors play a vital role in protecting the health and well-being of employees. By capturing and filtering airborne particles, they reduce the risk of respiratory issues and allergic reactions among workers, promoting a safer and healthier working environment.
Regulatory Compliance: The pharmaceutical industry is subject to strict regulations and guidelines regarding air quality and worker safety. Dust collectors help companies comply with these regulations by effectively controlling dust emissions.
Cost Savings: Implementing a dust collector system can lead to cost savings in the long run. By reducing product contamination and minimizing the likelihood of costly product recalls, companies can protect their reputation and avoid financial losses. Additionally, improved worker health and safety reduce absenteeism, enhance productivity, and lower healthcare expenses. Pharmaceutical dust may be an often overlooked aspect of the manufacturing process, but its impact on product quality, worker safety, and regulatory compliance cannot be understated. Dust collectors act as unsung heroes, diligently capturing and removing airborne particles, thereby minimizing contamination risks, ensuring workplace safety, and promoting regulatory compliance. Investing in dust collector systems is a proactive step that pharmaceutical companies can take to protect their products, employees, and bottom line. By leveraging these systems, the industry can achieve higher product quality, reduce the likelihood of accidents and product recalls, and create a safer working environment.
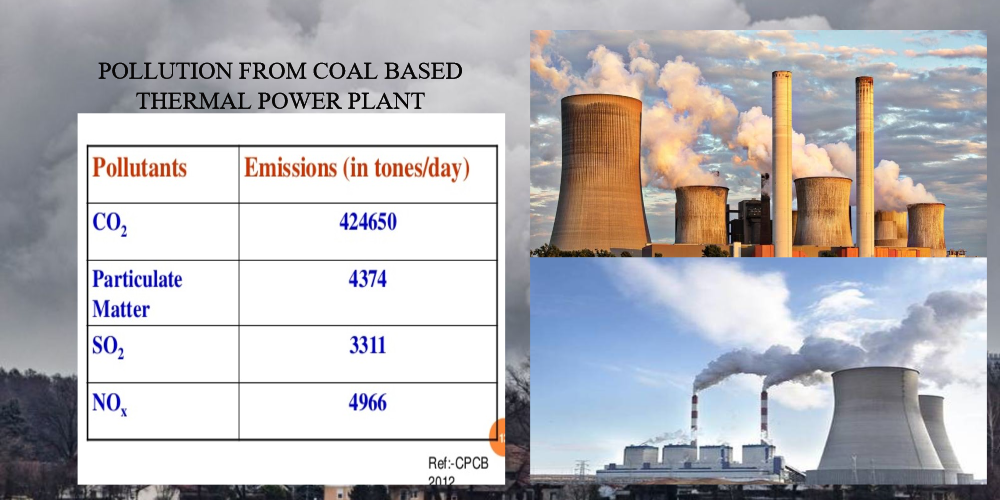
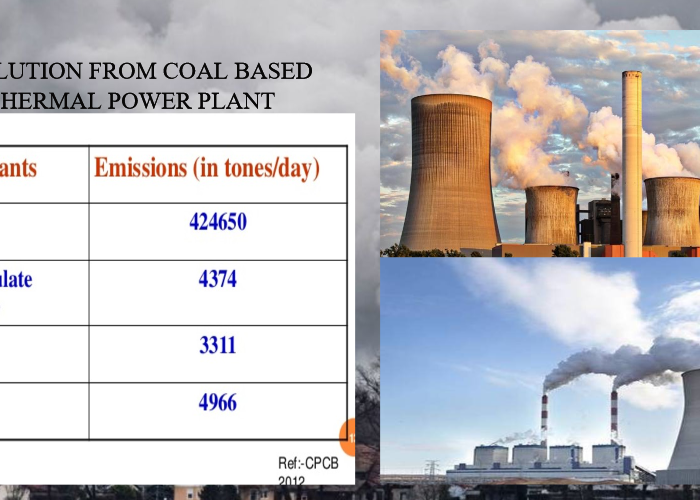
Thermal Power Plant Pollution
Thermal Power Plant Pollution
Thermal power plants gives out lot of gas which are harmful to our environment. Thermal power plant is used to converts heat energy into electric power. Chief justice of India SA Bobde said on Friday (29.2.20), he wanted all the thermal plants in the country shut to prevent environmental pollution. Bobde was dealing with a case from Uttarakhand where many projects had come under the court scanner along with Justices BR Gavai and Surya Kant. Thermal pollution is the degradation of local environment, in particular the localized waterways, were changed by discharge of waste water from power plant.
Effect on Atmosphere
Thermal power plant produce lot of greenhouse gases, which are by-products of burning fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide is one of the main gas that is released from burning of fossil fuels and it is the main reason for global warming. Thermal power plant is one of the reason to increase the carbon dioxide level throughout the world. Sulfur dioxide is another gas released from power plants. It is not a greenhouse gas, it gave indirect effects to atmosphere because it affect the scattering of sunlight. So it is considered as indirect greenhouse gas. This will return to earth as acid rain and will impact on ecosystem. The level of sulfur dioxide released from thermal power plants depend on the amount of sulfur dioxide released from thermal power plants depends on the amount of sulfur in the coal. The coal used in thermal power plant has an average between 0.1 and 3.5% of sulfur and the thermal power plants are the largest emitters of sulfur dioxide worldwide.
Nitrogen oxide are another gases that released in thermal power plants. It is one of the largest contributor to global nitrogen oxide levels. Both nitrous oxide and nitrogen oxides are not greenhouse gases, but it has an indirect effect on the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxide will cause respiratory issues and they combine with other atmospheric gases and moisture to form acid rain and smog. The other big pollutant to atmosphere is ash in the thermal Plants. Coal is used in thermal power generation which produce fine particles of ash will cause environmental problem. Ash will spread in the atmosphere will contains ash particles like silica, alumina, iron oxide, calcium, magnesium, lead, arsenic, cobalt and copper. Ash contain particulate matter known as PM2.5, are the particles less in diameter.
Effect on Local Environment
Thermal pollution is one the biggest problem in local environment. When the water in power plant is no longer usable, it gets discharged into local waterway. Wastewater generally have high temperature than local natural water, it can increase the temperature of water and it also have negative impact on local ecosystem. The released ash particles contain metal ions which can escape into local ecosystem and it also contain radioactive nuclides. Radioactive nuclides that emit radiation as they undergo radioactive decay through emission of alpha, beta or gamma particles. They affect the local environment from waterways, soil, vegetation and other living organisms.