Author: admin
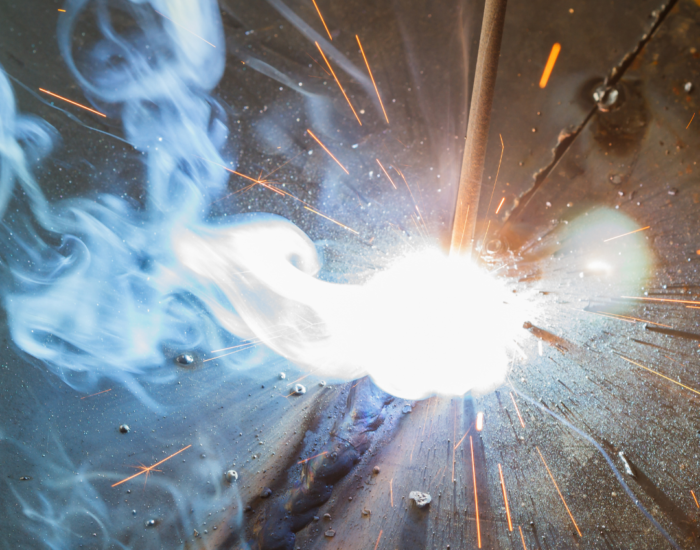
Exploring the Minuscule World of Welding Particles
Welding, the art of joining materials through intense heat and skillful manipulation, has been instrumental in shaping the modern world. From towering skyscrapers to intricate sculptures, welding has left its mark on everything we see around us. Yet, amidst the brilliance of welded creations, there exists a hidden world of particles that often goes unnoticed – welding fumes. These tiny particles, suspended in the air during welding processes, hold secrets that are both intriguing and concerning. In this article, we embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of welding fumes and delve into the size of the particles that compose them.
Welding Fumes and Their Composition:
Welding fumes are an assortment of tiny solid particles that are generated when welding or cutting metals. These fumes consist of various compounds, which include metallic oxides, gases, and particulate matter. However, it’s the particulate matter that captures our attention due to its unique size and characteristics.
The Scale of Welding Particles:
Welding particles are remarkably small, falling within the range of nanometers to micrometers. To put this into perspective, a single micrometer is a mere one-thousandth of a millimeter. Imagine a particle so minuscule that thousands could fit on the head of a pin!
Welding particles can be classified based on their size:
- Inhalable Particles (PM10): These are particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers or smaller. They are easily inhaled into the respiratory system, potentially reaching the deeper parts of the lungs.
- Respirable Particles (PM2.5): Even smaller, these particles have a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less. They are fine enough to bypass the body’s natural defense mechanisms penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream.
The Diverse Composition of Welding Particles:
Welding particles are not all created equal their composition can vary widely based on the type of welding process, the materials being welded, and the presence of coatings or contaminants. Some common constituents of welding fumes include:
- Metallic Oxides: Generated by the oxidation of metals during the welding process, these particles include compounds like iron oxide, aluminum oxide, and manganese oxide.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Certain welding processes release gases and vapors that can condense into fine particles. These compounds can have adverse health effects.
- Welding Rod Coatings: Many welding electrodes are coated to improve arc stability and weld quality. The coatings can release particles of various elements such as titanium, zinc, and copper.
- Base Metal: The base metal being welded can also contribute to the composition of welding fumes. For instance, welding stainless steel can release particles containing chromium and nickel.
Protecting Welders and Beyond:
The small size of welding particles plays a significant role in their potential health impact. Respirable particles, due to their size, can reach the alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs – and even enter the bloodstream. This can lead to various health issues, including respiratory irritation, lung diseases, and in some cases, systemic effects.
As a leading manufacturer of welding fume extractors, we take pride in our dedication to ensuring the well-being of welders and beyond. Our mission extends beyond crafting exceptional welding solutions – we are champions of health and safety in welding environments. Welding fumes might be hidden from the naked eye, but their impact is significant. The particles that compose these fumes are so small that they can infiltrate deep into our bodies, highlighting the importance of occupational safety in welding industries. As we marvel at the grandeur of welded structures, let’s not forget the microscopic world that accompanies them – a world that serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between human creativity and the need to safeguard our health.
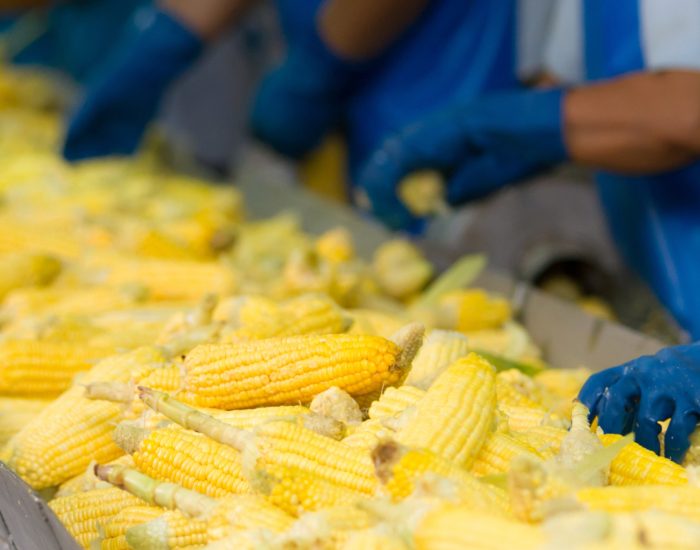
Optimizing Dust Collection in the Food Industry
When you think of a bustling food processing facility, the aroma of freshly prepared dishes and the rhythmic hum of machinery might come to mind. However, there’s another aspect of food production that’s equally important, yet often overlooked – dust collection. In the food industry, airborne dust particles generated during various processing stages can pose serious risks to both product quality and the health and safety of workers. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of optimizing dust collection in the food industry and the key ingredients for a successful recipe that ensures safety, efficiency, and compliance.
The Hidden Hazards of Food Processing Dust
It’s easy to dismiss dust as a minor inconvenience, but in reality, it’s a silent hazard that can lead to a range of issues. Dust particles generated during operations like grinding, mixing, and packaging can contaminate food products, compromise the hygiene of the processing environment, and even result in health problems for workers. This is particularly true for employees who are repeatedly exposed to airborne dust, as it can lead to respiratory issues such as allergies, asthma, and other chronic conditions.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
One of the main reasons for optimizing dust collection in the food industry is to adhere to regulatory standards. Food processing facilities are subject to strict regulations set by organizations such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Compliance with these regulations is not just a matter of avoiding fines; it’s about ensuring the health and safety of employees and consumers alike.
Key Ingredients for Optimizing Dust Collection
- Effective Dust Control Methods: Dust collection isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Different processing stages require different approaches. Our state-of-the-art dust collectors, tailored for the food industry, play a vital role in removing dust and ensuring a cleaner, safer environment. By implementing a combination of techniques, facilities can achieve optimal results.
- Regular Maintenance: Just like regularly checking the seasoning in a dish, maintenance of dust collection systems is crucial. Filters, fans, and ducts should be inspected and cleaned on a routine basis. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency and compromised air quality.
- Employee Training: A well-trained kitchen staff is essential for a smooth cooking process. Similarly, educating employees about the importance of dust collection, proper use of equipment, and the hazards of dust exposure is vital. When employees understand the risks and best practices, they can actively contribute to maintaining a clean and safe environment.
Dry Scrubber: Solution for Controlling Toxic Gas Emissions
In a world where industrial activities and human progress are inseparable, the challenge of managing environmental impacts becomes increasingly crucial. One of the most significant concerns is the release of toxic gases into the atmosphere, which poses serious threats to human health and the ecosystem. In this context, dry scrubbing has emerged as a powerful technique for mitigating toxic gas emissions, offering a promising solution to address this pressing issue.
Understanding the Problem: Toxic Gas Emissions
Toxic gas emissions are a result of various industrial processes, such as power generation, manufacturing, and chemical production. These gases, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and chlorine (Cl2), can have severe health implications for humans, contribute to air pollution, and harm ecosystems. As awareness of these risks grows, finding effective ways to reduce these emissions becomes imperative.
Introducing Dry Scrubbing
Dry scrubbing is an innovative technique designed to control and mitigate toxic gas emissions. Unlike traditional wet scrubbing methods that involve spraying a liquid solution to capture pollutants, dry scrubbing employs a solid sorbent material that reacts with and captures harmful gases.
Advantages of Dry Scrubbing
- Cost-Effectiveness: Dry scrubbing is often more cost-effective due to lower infrastructure and maintenance costs. It doesn’t require complex liquid handling systems or wastewater treatment facilities, making it an attractive option for industries looking to control emissions while minimizing operational expenses.
- Minimal Water Usage: Dry scrubbing is a waterless process. This not only conserves water resources but also eliminates concerns related to water disposal and contamination.
- Space Efficiency: Dry scrubbing systems are generally more compact, making them suitable for facilities with space limitations. This efficiency in space usage can be particularly valuable for retrofitting existing industrial units.
- Versatility: Dry scrubbing can be tailored to address specific pollutants by selecting the appropriate sorbent material. This flexibility allows industries to target multiple types of toxic gases with a single system.
Why is SO2 Scrubbing a Necessity?
In an age where environmental concerns and public health take center stage, the need for effective air pollution control measures has become more pressing than ever before. Among the many pollutants that contribute to poor air quality, sulfur dioxide (SO2) stands out as a particularly harmful substance. As we strive for a cleaner, healthier future, understanding why SO2 needs to be scrubbed from industrial emissions is of paramount importance.
The Dangers of Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Emissions:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor that is released into the atmosphere primarily through the combustion of fossil fuels containing sulfur, such as coal and oil. Major sources of SO2 emissions include power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles. While SO2 itself is not directly harmful in low concentrations, it can have serious consequences for both the environment and human health when released in larger amounts.
Environmental Impact:
- Acid Rain Formation: SO2 emissions can lead to the formation of acid rain when they combine with water vapor in the atmosphere. Acid rain poses a threat to aquatic ecosystems, forests, soil quality, and even buildings and infrastructure.
- Damage to Vegetation: Acid rain resulting from SO2 emissions can harm vegetation by damaging leaves, reducing photosynthesis, and limiting plant growth. This has a cascading effect on entire ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
- Destruction of Biodiversity: Acidification of aquatic environments due to acid rain harms aquatic life, disrupting the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems and leading to reduced biodiversity.
Health Impacts:
- Respiratory Issues: Inhalation of sulfur dioxide can cause a range of respiratory issues, including exacerbating asthma symptoms, aggravating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and increasing the risk of respiratory infections.
- Cardiovascular Problems: SO2 exposure has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, due to its ability to trigger inflammation and constrict blood vessels.
- Particulate Matter Formation: SO2 can react with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which is associated with a wide range of health problems, including lung cancer, heart disease, and premature death.
The Solution: SO2 Scrubbing:
SO2 scrubbing, also known as flue gas desulfurization (FGD), is a crucial technology used to remove sulfur dioxide from industrial emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. This process involves treating flue gases with substances that react with and remove the sulfur dioxide. There are various methods for SO2 scrubbing, including wet scrubbing and dry scrubbing.
Benefits of SO2 Scrubbing:
- Improved Air Quality: The primary benefit of SO2 scrubbing is the reduction of sulfur dioxide emissions, leading to improved air quality and a decrease in acid rain formation, thereby protecting both the environment and human health.
- Healthier Communities: By reducing SO2 emissions and their associated health impacts, SO2 scrubbing contributes to creating healthier communities with fewer cases of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Preservation of Ecosystems: SO2 scrubbing helps preserve ecosystems and biodiversity by reducing the harmful effects of acid rain on aquatic environments, forests, and soil quality.
Air Quality: Your Health’s Unsung Hero
Clean air is a fundamental requirement for sustaining life, yet it is often taken for granted. Every breath we take has the power to impact our health significantly. The quality of the air we breathe is closely intertwined with our well-being, making it crucial to understand the relationship between air quality and health. In this blog, we will explore the profound impact of air pollution on our bodies and delve into the importance of striving for cleaner air for a healthier future.
The Dangers of Air Pollution:
Air pollution is a silent menace that affects billions of people worldwide. It encompasses a range of pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds. Sources of air pollution vary from industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust to indoor pollutants like tobacco smoke and household chemicals. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants can lead to a multitude of health issues.
Respiratory Disorders:
Airborne pollutants can severely affect our respiratory system. Fine particulate matter, known as PM2.5, can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation and irritation. This can lead to respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Long-term exposure to polluted air may even contribute to the development of lung cancer.
Cardiovascular Complications:
Air pollution doesn’t limit its impact on the respiratory system alone; it also poses significant risks to cardiovascular health. Particulate matter and pollutants like nitrogen dioxide can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and oxidative stress. This can lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and those with pre-existing heart conditions, are particularly susceptible to these risks.
Impact on Children’s Health:
Children are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of air pollution. Their developing lungs and immune systems make them more susceptible to respiratory infections and long-term complications. Exposure to polluted air during early childhood can impair lung growth, leading to reduced lung function in adulthood. Additionally, studies have linked air pollution to neurodevelopmental disorders and cognitive impairments in children.
The Importance of Clean Air:
Recognizing the critical role of clean air in maintaining good health, efforts must be made on various fronts to improve air quality. Government regulations, technological advancements, and individual actions are vital in reducing air pollution.